Siemens Digital Production
Interaction with Simplifier in the smart factory
1. Initial Situation
The manufacturing industry enormously benefits from the potential of digital transformation. Technologies like sensor technology, robotics, AR and VR, that enable high-quality data acquisition and evaluation, guarantee a efficient production in a batch size of 1, high productivity, lower production costs, higher competitiveness and zero downtimes.
For its division Process Industries and Drives in Nuremberg, Siemens AG intends to leverage the advantages of these innovative technologies. In this case, the focus concentrates on customer-specific projects with a high level of manual production, which means that people still play a major role in the process. For this reason, IT must enable the workers to interact with the systems and with the machines as well.

2. Challenge
The manufacturing process at the Siemens factory in Nuremberg was characterized by a lot of paper-based work. For the factory workers, the acquisition and transfer of information was associated with a huge workload. Either there were many different data sources or the quality of the data was lacking. Isolated solutions impeded the transparency and quality of the data and were also partly incompatible with ERP systems such as SAP.
As a result, a standardized database was not available for the manufacturing processes. Duplicate records and additional work therefore occurred daily. Malfunctions, for example, had to be logged using several tools so that relevant departments could invoice costs, eliminate technical errors or purchase spare parts.
Defined goals (mid- to longterm)
R2D – Road to Digital Production
 The applications, which have been developed for Siemens on Simplfier basis, are also an integral component of a research project of the Bavarian State Ministry. Within a Cyber-Physical Production System (CPPS) the productive use of the application in the manufacturing process has been tested.
The applications, which have been developed for Siemens on Simplfier basis, are also an integral component of a research project of the Bavarian State Ministry. Within a Cyber-Physical Production System (CPPS) the productive use of the application in the manufacturing process has been tested.3. Solution
Using the low-code platform Simplifier, integrated business and IoT applications can be created in a minimum of time. The platform uses existing IT infrastructure and integrates existing systems such as SAP databases as well as Siemens’ Mindsphere IoT platform. So called connectors transfer the data, that can be used and controlled within a mobile application.
Two applications examples in use:
Non Conformance (NC) App
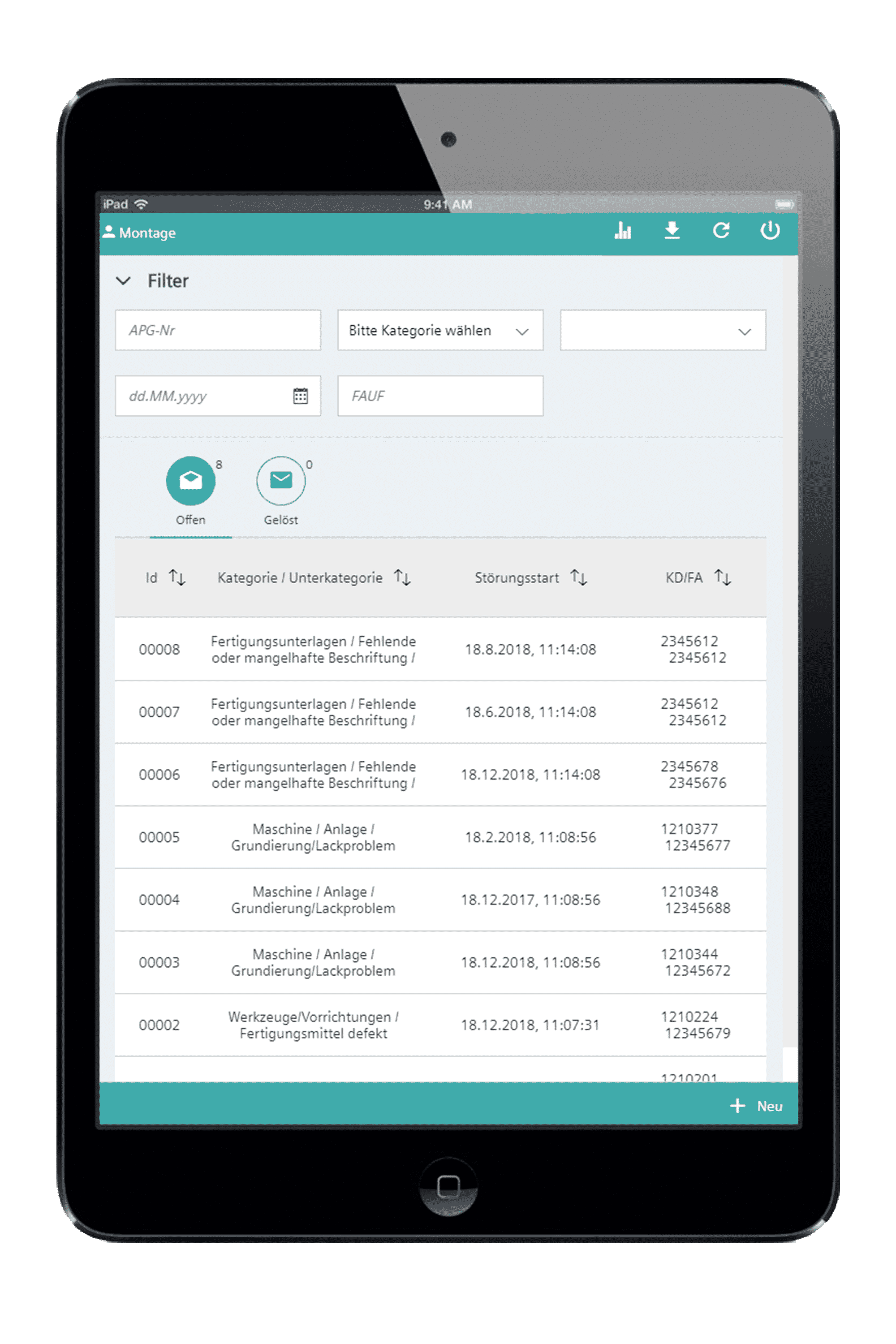
This IoT application was built on Simplifier and is used to log error messages that occur during the manufacturing process. For a smarter final inspection of a product, data exchange should be easier in case of a malfunction. The worker has access to existing product data from the system database and has to enter only a few details about the malfunction – quickly and easily via mobile device. Further information will also be stored in the system so that all relevant data is available and can be used during the troubleshooting process.
SIPRO App
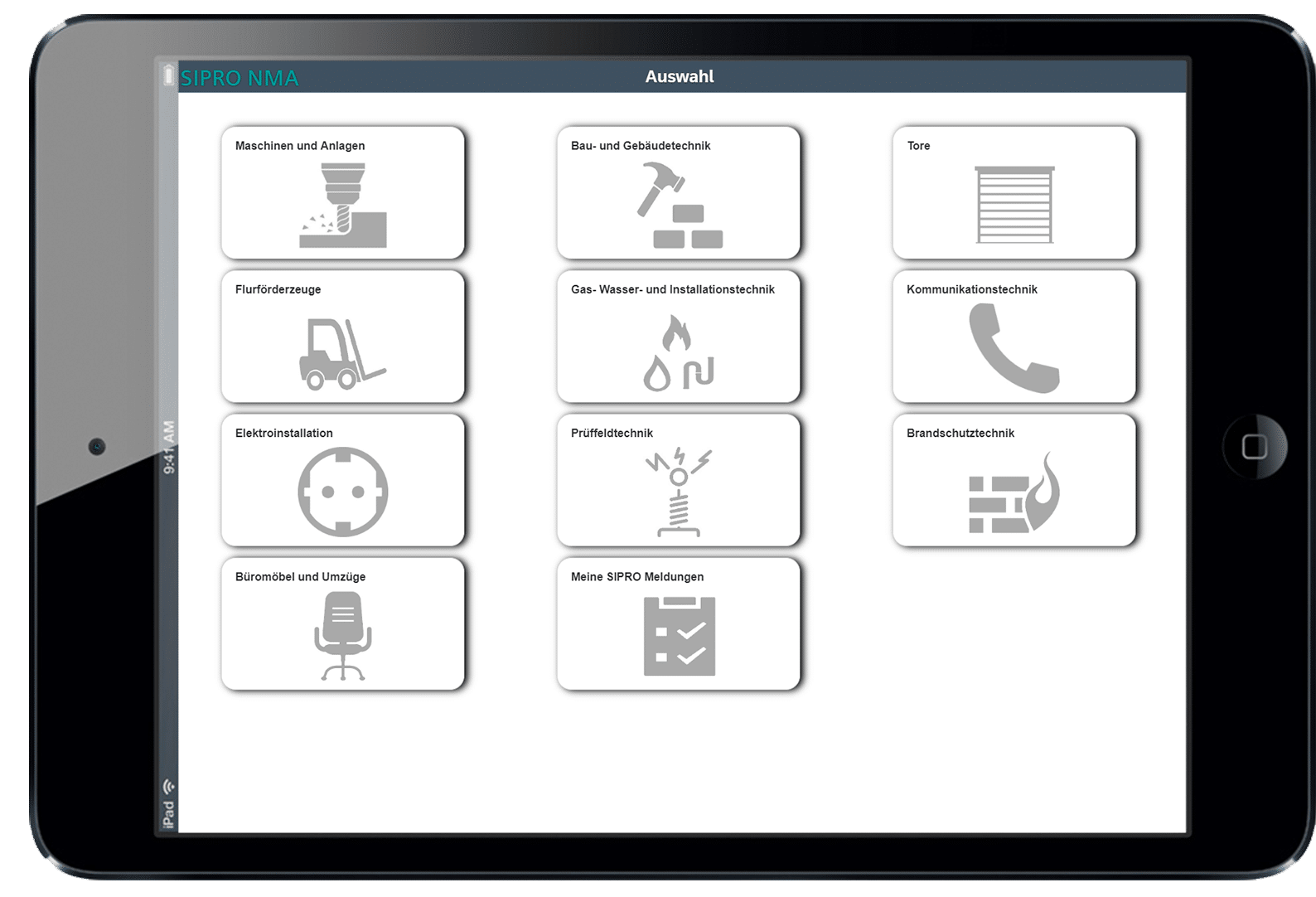
Opposite to the NC-App, SIPRO does not log malfunctions in the project, but defects in machine tools, buildings, telephone systems etc.. SIPRO-App has been used for several years, but the technology that was used became outdated and should therefore be replaced. Simplifier enabled a smooth and quick creation of the same app and via standardized connectors the SAP PM system could be integrated without any problems. The SIPRO app is already the second application that communicates with SAP and has gone live in the factory within a very short time.
4. Results
ROI attained in less than 12 months
8 Apps live within 6 months
First app already created and deployed in 24h
5 employees in less 2 weeks empowered to create apps
Employees benefit from this:
For the workers, the digitization of production has improved a lot. Data acquisition using pen and paper has become a matter of the past. System integration with Simplifier, however, enables them to interact with the IT system despite the digital processes. Thanks to the innovative technologies and the user-friendly handling of the smart devices, the acceptance of use by the workers is very high. The applications were immediately accepted, but not just that. The use of the Simplifier enabled the factory workers to build their own applications for their needs. Moreover, the mobile data acquisition also simplifies the process flow in all divisions. The consistency of the data acquisition also increases the data quality. This enables the analysis of nonconforming processes and the identification of correlations in the manufacturing processes.