Rapid Application Development (RAD)
MODERN SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a programming approach based on a continuous development environment. This means that changes can be implemented faster than with the traditional method of application development.
HISTORY
In the 1970s, Brian Gallagher, Alex Balchin, Barry Boehm and Scott Shultz developed the Rapid Application Development approach with the aim of speeding up and making the previous complex software development process more flexible.
Rapid application development only became famous a few years later. In the early 1990s James Martin, a British information technology consultant and author, developed a method based on iterative development and prototyping.
To this day, the Rapid Application Development approach has been widely used in the development environment. For example, the low-code platform Simplifier provides a technology which allows integrated applications to be configured in a resource-saving manner. Reusable building blocks and the use of existing IT systems ensure the necessary efficiency when digitizing business processes. Thanks to the Rapid Application Development approach and rapid prototyping, the Simplifier makes it possible to effectively develop a comprehensive and performance-oriented application in less time.

METHOD
Entry into fast application development is usually done in a cyclical process, which comprises four basic phases. The aim of Rapid Application Development is to develop an executable prototype of the software as quickly as possible, in accordance with the user’s requirements. In order to guarantee a fast delivery, the developers fall back on software construction kits.
Requirements Planning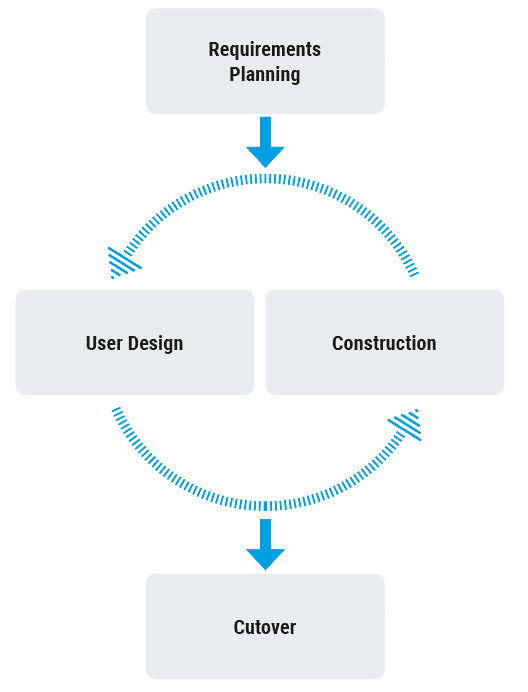
In the initial phase, designers, developers and users make a rough agreement on the scope of the project and prioritize the application requirements so that prototyping can be started in the future phases. In the first phase, both developers and users are allowed to talk and communicate with each other. In the subsequent phases it will be omitted.
Based on the list of application requirements with prioritization, the developers design an executable prototype of the software as soon as possible. They can use a “software kit” to quickly assemble the most important basic requirements.
User Design
In the second phase, feedback from users is collected after completion of the first prototype. The focus is on defining the system architecture. Requirements are supplemented or refined. This makes it possible to create initial modelling. This step is repeated as often as necessary to further develop the project. In contrast to the first, the second phase serves more for a user’s monologue.
Construction
Once the basic user and system design has started, most of the actual application coding, testing and integration takes place in the design phase. Together with the user design, the construction phase is repeated as often as necessary because new components are needed or changes are made to meet the project’s requirements. The user’s new requirements are optimized and added to the software in a short development cycle, usually between one day and up to three weeks. This approach creates new and improved versions of the software in every iteration.
Cutover
The final phase, the cutover, allows the development team to move the components into a live production environment where all necessary tests or team training can be carried out.
Due to the cyclical process, Rapid Application Development differs significantly from the waterfall model. In the classic waterfall model, each phase of development forms an independent unit. After completion of each unit, the next step is considered. As with a waterfall, it is no longer possible to return to a previous phase.
In contrast to the Rapid Application Development approach, this allows each step in the waterfall modernization process an enormous amount of time to avoid errors. As a result, software development is slower and takes a lot of time and energy to develop. Errors in development or incorrect requirements can quickly make a project fail in the waterfall model.
USE OF RAPID PROTOTYPING
While different forms of rapid application development highlight slightly different concepts and design methods, the intensive use of prototypes is consistent across all forms. The use of prototypes provides a number of unique advantages throughout the entire development cycle:
User Involvement
In contrast to a traditional waterfall model, where the design team discusses with users what features or implementations are required and has to plan specifications around these ideas, a RAD prototype allows users to use the software immediately. The feedback can thus be given to a live system and does not include the abstract evaluations of a design document.
Doability
Prototyping enables the development team to assess the feasibility of a particularly complex or risky component directly on site. The early detection and processing of complex systems in the development cycle makes the software more robust, less error-prone and better structured for future design enhancements.
Error Reduction & Debugging
With rapid prototyping releases during a project, it is far more likely that errors can be detected and eliminated much earlier in the development cycle.
THE ADVANTAGES OF RAPID APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
Rapid Application Development’s approach requires very little pre-planning and preparatory work and ensures that productive results are achieved more quickly. Thanks to the saved time and the parallel development of the different software development phases, this form of software development means that a ready-to-use software can usually be delivered in less than 120 days. Further advantages of Rapid Application Development at a glance:

Fast generation of productive code
The Rapid Application Development approach enables rapid creation of working code and prototypes. The processes are fluid and merge into each other, which not only leads to greater transparency but also to a faster development time.

Measurable progress
With frequent iterations, components and prototypes that are drawn in length, the progress of the overall project, but also of smaller segments, can be easily measured and evaluated. This means that schedules and budgets can be maintained.

Higher quality
Due to the constant interaction between users and the developing prototype, a higher quality can be ensured by the Rapid Application Development approach. This makes the software more user-friendly.

Fast, constant user feedback
During development and prototyping, it is invaluable to receive feedback from users who interact directly with the application, both easily and frequently. The Rapid Application Development approach enables almost constant user guidance and feedback through frequent iterations and prototype approvals.

Early system integration
While most software projects traditionally have to wait until the end of their lifecycle to begin integration with other systems or services, a Rapid Application Development application is integrated almost immediately. Through early integration within a prototype, the Rapid Application Development System quickly detects all errors or complications within the integration and forces immediate solutions.

Easy adaptability
During development, software is a fairly customizable form. Since code can be changed at any time and this leads to changes in the system or even new components are generated, it is advantageous for the development team to use this flexibility early and frequently by iterating and prototyping potential concepts or ideas throughout the entire development process.

Risk control
By focusing on the development of incremental units, the chances of catastrophic failures are reduced.
THIS IS HOW WE ACCELERATE YOUR SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
MVC-Softwareconcept par excellence
STATE-OF-THE-ART FRAMEWORKS IN SIMPLIFIER APPLICATION













































